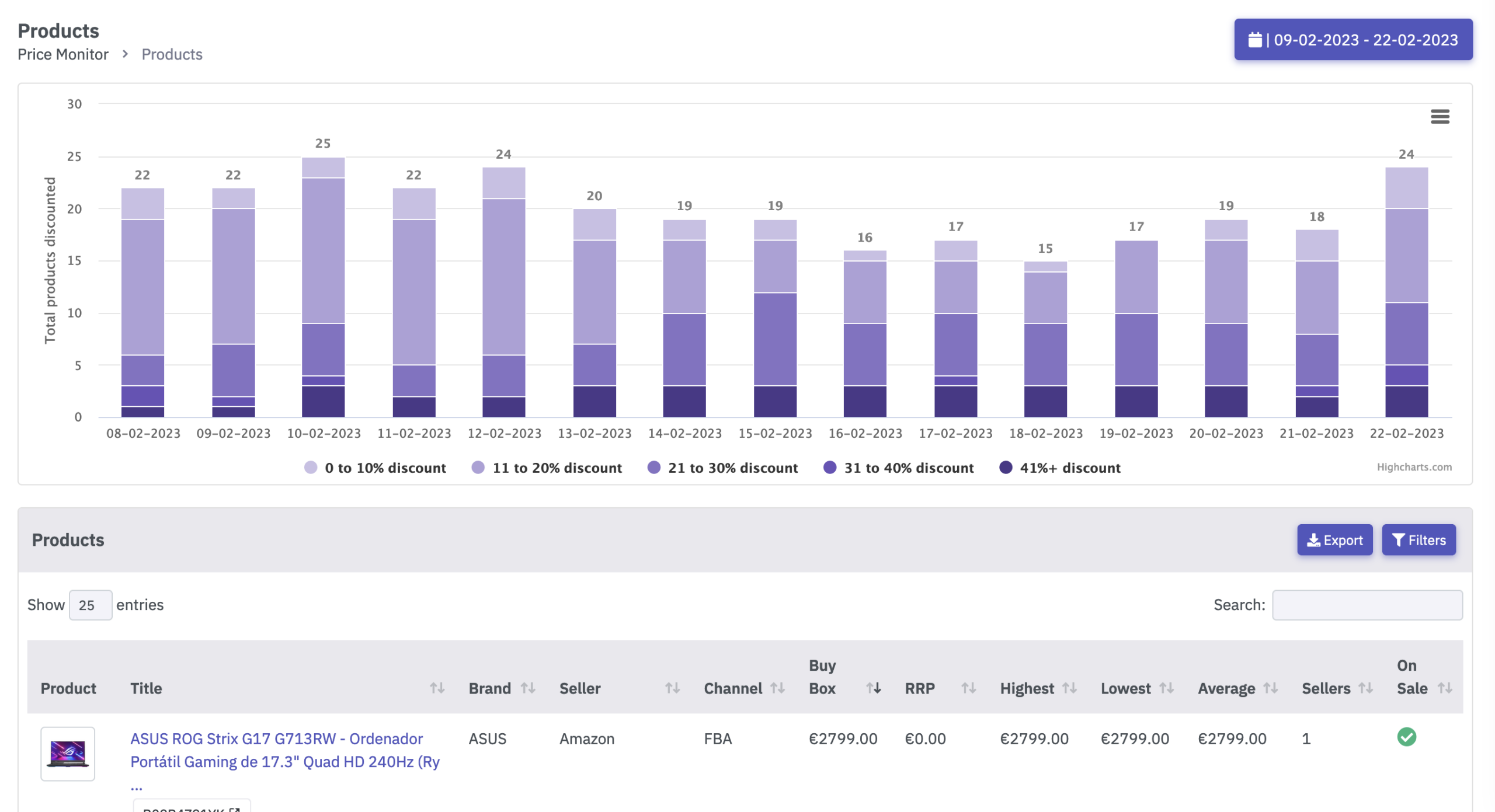
The product life cycle (PLC) is an important concept to successfully establish products and services in the market. The PLC consists of different phases that allow managers to visualize the projected development of sales and profits of their product portfolio.
This serves to plan the necessary marketing strategies to extend the life cycle in the phases in which the profits and market shares are higher.
Index
What is the product life cycle?
The product life cycle is the stages through which a product passes from its launch to the market to its withdrawal or replacement.
The basic PLC model comprises five phases:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Saturation
- Slope
Phase 1: Introduction
The first phase is the entrance of the product to the market . From this moment, customers can acquire the product.
In this phase the promotion is essential so that consumers know the new offer. Therefore, an effective marketing strategy must be developed.
Depending on the sector, the type of product and the marketing strategy, often the products are announced before the launch of real sales and are sometimes offered for pre-periods.
The launch or introduction phase to the market is costs and, therefore, negatively affects the company's profit curve. The reason? The company must first invest more money in marketing activities than they can win with the new product. But, as soon as the company begins to generate more sales, earnings also begin to increase, which results in a positive profit relationship.
This first stage ends when the equilibrium point is reached, that is, when sales revenues cover the cost of selling the product.
Phase 2: Growth
This phase is characterized by a continuous increase in sales as the product gains acceptance and more customers buy it .
Upon reaching this phase, the company's approach changes, who is no longer focused only on marketing but also on the fulfillment of demand forecasts to ensure that the product is available.
But, competitors also appear and if they see an attractive opportunity to enter the market, they will launch their own versions of the product. Many times, this generates price wars and imitations, which can harm the long -term success of the product.
Phase 3: maturity
Most of the products reach their most profitable status in this phase, since they have managed to establish themselves in the market and, therefore, they no longer need to be promoted with so much effort.
In the maturity phase, growth is almost exclusively displacing customers of competitors. Brands need to constantly build and focus on their own brand and marketing messages so as not to become victims of these approaches.
Phase 4: saturation
When saturation is reached, billing and gains and market growth decrease . Here, the objective is to offer cheaper products than competitors to increase profits while sales stagnate.
If the leadership in costs is achieved and maintained, the saturation phase allows companies to ensure their market share and resist the attempts of competitors to start price wars in their industry.
Phase 5: Decline
Finally, the product life cycle ends with the decline phase. It is characterized by a growing loss of profits, billing and market share , which are no longer compensated with marketing efforts.
The approach in this phase is to launch innovations to the market to meet the current needs of customers. That is, if it is not decided to remove the product from the market, it can evolve to reposition it.
When the decline phase is reached, the basic model of the product life cycle ends. The result? The product "dies."
The BCG matrix
The BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix is a tool that allows companies to analyze and manage their product portfolio . It is based on two main dimensions: the relative market share and market growth. From these dimensions, four categories of products arise:
Stars (STARS): products with high market share and high growth. They represent opportunities for growth and expansion, so you must invest in them to maximize their potential.
Questions (Question Marks): products with low market share, but in high growth markets. They are usually in the initial stage of their life cycle and require marketing investments to increase their market share.
Dairy cows ( Cash COWS ): products with high market share, but in low growth markets. They generate constant income and high benefits due to their relatively low operating costs. The strategy to be used is to maintain and exploit these products to finance other areas of the business.
Dogs (poor dogs): products with low market share and low growth. They often generate losses and represent a load for the company. It is best to discontinue or relaunch them with new features to try to revitalize them.
Factors that influence the product life cycle
The factors that influence the product life cycle are internal and external. Let's see what it is:
Internal factors
- Price strategy: Adjusting prices strategically can prolong or shorten the life of the product. Competitive prices increase demand, while high prices limit it.
- Branding campaigns: Investing in marketing and in the construction of a solid brand can increase notoriety and loyalty towards the product, positively affecting its life cycle.
- Post -sales activities: Offering a good after -sales service can improve customer satisfaction and prolong the maturity phase of the product.
External factors
- Political and legal context: changes in government regulations and policies can influence the product life cycle. For example, new environmental laws can force market products.
- Economic conditions: The state of the economy can affect the purchasing power of consumers and, therefore, the demand for the product. Economic recessions shorten the lives of many products.
- Competitors input: The appearance of new competitors or substitute products can accelerate the decline phase of a product by reducing its market share.
- Technological innovation: Technological advances can make existing products become obsolete more quickly, shortening their life cycle.
Conclusion
The product life cycle (PLC) is a fundamental concept in product management and marketing. Describe the different stages through which a product is going through from its launch to its market withdrawal. Understanding this cycle is important for companies to make strategic decisions and optimize the profitability of their products.
Each of the PLC phases implies specific challenges and opportunities in terms of sales, competition, costs and benefits. The company must constantly adapt its product, price, promotion and distribution strategies to successfully travel the complete cycle.

